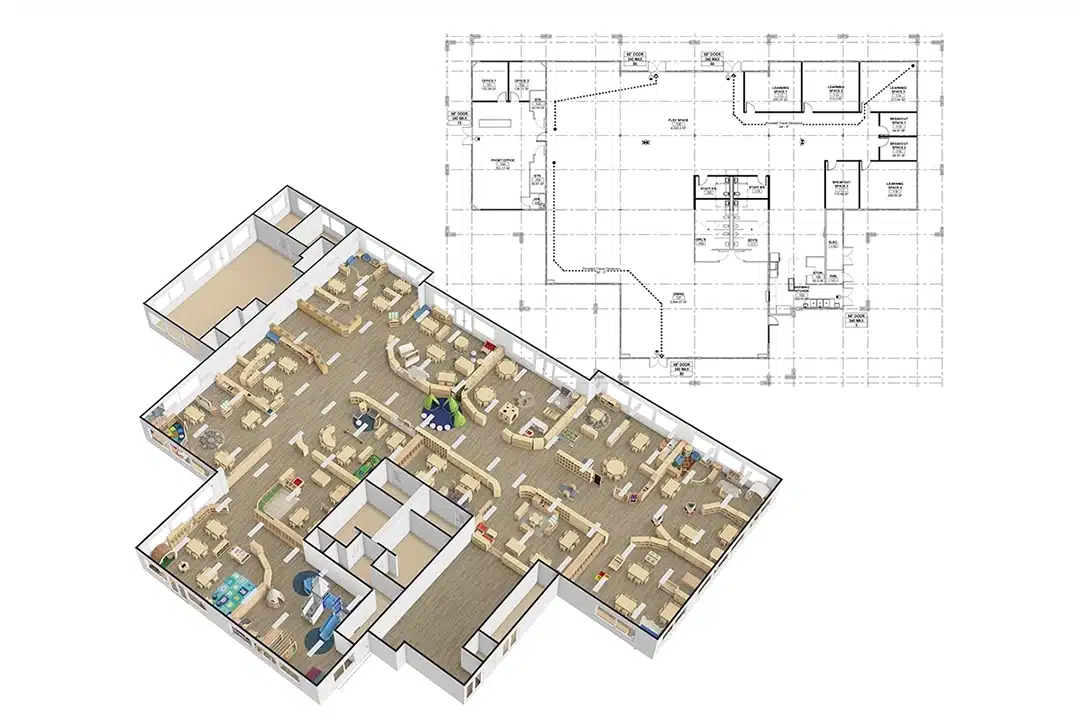
Have you ever wondered how classroom space affects students’ learning? Does a cramped, traditional classroom layout hinder creativity and engagement? What if vertical classroom spaces could change the entire educational experience?
In traditional classrooms, the focus tends to be on horizontal space. However, vertical classroom spaces are gaining attention for their ability to foster creativity, improve organization, and enhance the learning environment. Educators can create dynamic and engaging environments that actively support students’ cognitive and physical growth by utilizing vertical spaces- such as walls, shelving, and overhead storage.
Are you ready to learn how vertical classroom spaces could make a difference in your school or kindergarten? Let’s dive in!
What Are Vertical Classroom Spaces?
Vertical classroom spaces represent a design shift in how classrooms are structured. Instead of following the traditional horizontal layout of rows of desks, vertical classroom designs use multi-level or tiered structures that optimize available space. This can include everything from mezzanine levels to tiered seating areas, adjustable platforms, or even elevated spaces for group activities. Using height and depth, these classrooms provide more open and flexible learning environments, encouraging creativity, collaboration, and student interaction.

Historical Evolution of Classroom Design
The classroom has evolved drastically from the early 20th century, when traditional rows of desks facing a teacher’s podium were the standard. These layouts were designed for passive learning, where students were largely expected to absorb information passively from the teacher. However, the need for more dynamic classroom spaces became evident with the advancement of educational theories emphasizing active learning, collaboration, and the importance of student engagement. Vertical classroom designs emerged as a solution to maximize space and encourage more active, participatory learning, especially in urban areas where school buildings face space constraints.
Benefits of Vertical Classroom Spaces
The benefits of vertical classroom spaces extend beyond just physical space. The layout can enhance student engagement, foster collaborative learning, and improve cognitive outcomes. Here are some key benefits:
- Increased Student Engagement: Vertical spaces create a more immersive learning environment. Students are no longer limited to sitting in rows or facing the front. They can work in various configurations, all while keeping their attention focused on different areas of the room.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Vertical classrooms promote group work and cooperative learning. With movable seating arrangements and accessible workstations, students can easily collaborate on projects, share ideas, and solve problems.
- Improved Flexibility: Teachers can quickly rearrange the classroom for different lessons, from lectures to hands-on activities. Vertical spaces allow for adaptive teaching methods, making it easier to engage different learning styles.
- Optimized Use of Space: Vertical classroom layouts are designed to maximize every inch of available space. Shelves, tall storage units, and even walls can be used for educational purposes, reducing clutter and creating a more organized, functional room.

Strategies and Ideas for Creating Vertical Learning Spaces
However, the pivotal question is whether these displays lean towards interactivity or passivity. In their illuminating book, “Through a Child’s Eyes: Inspiring Learning and Wonder through Classroom Design,” Dr. Sandra Duncan, Jody Martin, and Sally Haughey urge educators to transform passive wall exhibits into interactive hubs for young minds. Reframe walls not merely as platforms to exhibit items but as zones for children to interact, collaborate, experiment, and learn.
Envision a vertical learning environment—an upright surface adorned with two- and three-dimensional elements that beckon children to explore, manipulate, interact, and construct knowledge.
These vertical learning spaces cater to all age brackets, even the youngest learners. Their design flexibility allows for quick setups or intricate arrangements, using resources ranging from the readily available to those demanding a bit more investment. The materials encompass an array of textures—wood, PVC piping, metal roofing, fabric, magnetic boards, carpet fragments, and curtain rods. Here’s a glimpse of strategies and ideas for crafting engaging vertical learning spaces:
- Elevate Accessibility: Position installations at children’s eye level, ensuring easy reach and engagement. For side-by-side activities, provide at least 40″ width for infants, toddlers, and twos; 50″ for preschoolers; and 60″ for young school-age children (Reddick & Bartlett, 1994).
- Authenticity Reigns: Opt for natural and genuine materials that resonate with the child’s world, steering away from plastic artifacts.
- Sturdy Craftsmanship: Construct robust surfaces and fixtures capable of enduring enthusiastic interactions from many young hands.
- Strategic Placement: Install these learning havens away from high-traffic zones and entrances, ensuring safety and a focused environment.
- Age-Appropriate Materials: Prioritize safety by selecting materials suitable for the children’s age and skill level, fostering unhindered exploration.
Design Principles Behind Vertical Classrooms
Successful vertical classroom designs follow several core principles:
- Clear Sightlines: Vertical layouts ensure that all students have a clear view of the teacher and learning materials, regardless of where they are in the classroom.
- Modular Design: Flexibility is built into the design, with modular furniture that can be rearranged to suit different teaching and learning scenarios.
- Open Space: Focusing on open, airy spaces helps students feel less confined and promotes a sense of freedom, reducing stress and fostering creative thinking.
- Technology Integration: Vertical classrooms often integrate cutting-edge technology, such as interactive whiteboards, projection screens, and digital devices, to complement the learning experience.

4 Reasons to Integrate Vertical Learning into Classroom Dynamics and Design
As educators nurturing early childhood development, we comprehend the significance of hands-on, experiential learning. A substantial share of these immersive encounters occurs on flat surfaces—tables and floors. Yet, why limit engagement to the horizontal plane when the vertical expanse (i.e., walls) beckons? Below are four reasons advocating the integration of vertical learning environments into our classroom dynamics and design:
- Midline Mastery: Crossing the midline—a virtual line bisecting the body—facilitates interhemispheric communication in the brain, which is pivotal for holistic development. This crossing primes children for reading, necessitating smooth left-to-right eye movements. Difficulty in midline crossing can impede coordination and hinder advanced cognitive skills, including reading.
- Spatial Intelligence: Interacting with vertical surfaces fosters spatial awareness, acquainting children with concepts like left-right, up-down, and high-low. Elevating the surface at eye level sharpens their grasp of spatial relationships.
- Fine-Tuning Proprioception: The body’s unconscious understanding of spatial movement and orientation is enhanced by sensory-integrated experiences. Vertical interactions bolster this kinesthetic awareness, promoting stability and body orientation.
- Affordance Awakens Curiosity: Psychologist James Jerome Gibson’s notion of “affordances” suggests that environmental cues invite actions. Vertical learning environments extend an irresistible invitation to explore, offering objects to manipulate, investigate, and ponder.

Creating a Vertical-Walled Classroom Environment
Crafting vertical wall environments encapsulates innovation and excitement. Draw inspiration from these concepts to transform discarded furniture, worn-out pieces, or modest construction materials into captivating vertical learning spaces.
1: Metallic Magic
Metallic magnet walls, suited for young and older learners, stand sturdy against inevitable childhood zeal. The tangible engagement between the two boys, absorbed in conversation, exemplifies the cognitive engagement fostered by such spaces. A sheet of metal roofing, procured from the local hardware store, serves as the foundation. Cut it to size with tin snips, securing it to the wall using heavy-duty screws. Trimming edges with a furring strip conceals sharp edges.
2: Baking Pan Brilliance
Designed for young children’s innate attachment and detachment drive, this vertical learning arena celebrates the allure of metal cookie sheets. These are mounted with metal screws, showcasing magnetic tape-clad puzzle parts. The result? A captivating platform encouraging pincer grip practice as children manipulate farm animals.
3: World on the Wall
This concept reflects children’s fascination with minuscule worlds and transforms a wall into an immersive canvas. Dollhouses and barns mounted precisely cultivate creativity, decision-making, and exploration. The drawer below the dollhouse, repurposed from an end table, doubles as a storage space, marrying practicality with imaginative play.
4: Pipes & Curves
Large PVC pipes, meticulously assembled, fashion an educational haven for infants and toddlers. The rhythmic act of dropping balls and observing their trajectory nurtures cause-and-effect cognition, spatial understanding, and core muscle development. Installing this environment is straightforward—purchase pipes, clamps, and screws, and let a battery-powered drill complete the job.
5: Sculptural Learning
Recognizing children’s intrinsic drive to explore through movement, this design hinges on curlers, transforming them into vertical learning elements. Constructing spatial understanding, dexterity, and motor skills, this approach resonates with Dr. Magda Gerber’s philosophy of embracing natural learning through exploration.
Traditional Classroom Settings vs. Vertical Classroom Spaces
| Aspect | Traditional Classroom Settings | Vertical Classroom Spaces |
|---|---|---|
| Seating Arrangement | Rows of desks facing the front | Modular, flexible seating |
| Teacher-Student Interaction | Teacher at the front, limited interaction | Open, teacher can move among students |
| Space Utilization | Limited, often crowded | Maximal use of vertical and horizontal space |
| Student Engagement | Passive listening | Active participation, group work |
| Learning Resources | Stored on shelves or desks | Walls and vertical surfaces utilized for resources |
| Adaptability | Fixed classroom setup | Easy to reconfigure for different activities |
Enhancing Collaboration and Engagement in Vertical Classrooms
Vertical classroom spaces provide an excellent platform for enhancing student collaboration and engagement. The layout of these classrooms encourages students to work together in different configurations rather than being confined to rows of desks. Students often feel isolated or detached from their peers in a traditional classroom. However, the arrangement fosters community in vertical classrooms, where students can easily share ideas, collaborate on projects, and actively participate in discussions.
In these spaces, movement becomes an essential part of the learning process. Students can work in groups, move to different workstations, or even present their work on vertical surfaces, ensuring that every student remains actively engaged in the learning process. By breaking down the traditional boundaries, vertical classrooms make it easier for students to connect, interact, and contribute to their learning environment.
Key Benefits of Vertical Classroom Spaces on Engagement:
- Flexible seating arrangements for group work
- Use of vertical surfaces for interactive learning
- Increased student participation and interaction
- Facilitates hands-on, project-based learning

Vertical Classroom Spaces and Technology Integration
Technology is an essential element in modern education, and vertical classroom spaces are designed to integrate technological tools that enhance the learning experience. These classrooms often use walls as interactive spaces with smartboards, digital displays, or augmented reality features. These technologies enable students to engage with learning materials innovatively, whether through interactive lessons, real-time feedback, or online collaborative projects.
The vertical design also allows for technology placement at varying heights, enabling students to interact with devices from different angles and positions. This contributes to a more immersive and engaging learning environment. Additionally, technology integration in vertical classrooms encourages students to develop digital literacy skills, better preparing them for future career demands.
How Technology Benefits Vertical Classrooms:
- Real-time feedback via digital tools
- Interactive learning through AR and VR
- Seamless access to online resources
- Enhanced student-teacher interaction via smart boards

Vertical Classroom Spaces and Montessori & Reggio Approaches
Vertical classroom spaces offer a natural fit for educators and administrators who embrace the Montessori and Reggio Emilia teaching methods. Both educational philosophies focus on child-centered learning and creating environments that allow children to explore, discover, and learn independently.
In a Montessori classroom, vertical elements such as shelves and workspaces enable children to choose their activities, access learning materials independently, and engage in self-directed learning. The vertical design allows children to move between different learning stations, encouraging exploration and autonomy.
Similarly, Reggio Emilia classrooms are known for their emphasis on the environment as the “third teacher.” Vertical spaces allow children to engage with their surroundings meaningfully, using their height to interact with objects, art displays, and educational tools placed within their reach.
Integrating vertical spaces can enrich the learning experience and support Montessori and Reggio teaching principles in kindergartens and preschools.

Vertical Classrooms in STEM Education
STEM education (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) requires innovative teaching methods and hands-on learning experiences that encourage problem-solving and experimentation. Vertical classroom spaces are particularly well-suited to STEM education, offering ample room for practical, interactive learning activities.
In a vertical classroom, students can work in teams to design experiments, build prototypes, or engage in collaborative problem-solving tasks. The flexibility of the space allows teachers to create different zones for various activities, such as lecture areas, lab workstations, and group project zones. This ensures that STEM students have the physical and intellectual space to experiment, collaborate, and innovate.
The multi-level design of vertical classrooms supports the dynamic nature of STEM education by allowing students to collaborate across different levels of complexity. For example, a student working on advanced coding projects may be able to interact with peers who are conducting physical experiments or working on engineering challenges, creating a cross-disciplinary learning experience.
Challenges and Considerations for Adopting Vertical Classroom Spaces
While the benefits of vertical classroom spaces are clear, there are several challenges to consider when adopting this design:
- Cost: Designing and building vertical classroom spaces can be expensive due to the need for custom preschool furniture, structural modifications, and advanced technology. Schools with tight budgets may find it difficult to make this transition.
- Accessibility: Ensuring that all students can access and benefit from vertical classroom spaces is crucial. Design considerations must be made to accommodate students with physical disabilities or mobility challenges.
- Acoustics: The multi-level design can sometimes result in poor acoustics, where sounds echo or become muffled, making it difficult for students to hear the teacher or each other. Effective soundproofing is essential in such spaces.
- Space Constraints: Not all schools have the physical space to implement vertical designs. Urban schools, in particular, may face difficulties retrofitting existing buildings to accommodate tiered seating and elevated areas.

Training and Professional Development for Educators in Vertical Classrooms
One key factor in successfully adopting vertical classroom spaces is educator training. Teachers must understand how to use the space effectively to foster collaboration and engagement. Professional development programs should focus on designing lessons that take advantage of the unique features of vertical classrooms, such as modular furniture, wall-mounted resources, and flexible seating.
Teachers also need to be trained to incorporate technology into these spaces. Familiarizing educators with new tools, such as interactive screens and digital resources, will allow them to fully utilize the vertical design and create more engaging lessons.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- How do vertical classrooms enhance student engagement?
The flexibility of vertical spaces encourages active participation and collaboration, leading to improved engagement and better learning outcomes. - What role does technology play in vertical classroom spaces?
Technology integrates seamlessly into vertical classrooms, supporting interactive lessons, personalized learning, and collaborative activities through digital tools and smart devices. - What challenges do schools face when adopting vertical classrooms?
Challenges include cost, accessibility, acoustics, and the physical constraints of existing buildings that may not be able to accommodate such designs. - How can teachers adapt to vertical classroom spaces?
Teachers need specialized training to use the space effectively, incorporating flexible teaching methods and leveraging technology to support a dynamic learning environment. - Are vertical classrooms suitable for all types of education?
Yes, vertical classrooms can be adapted to various educational levels, including primary, secondary, and higher education. - How can schools transition to vertical classroom designs?
Schools can consult with architects, invest in flexible furniture, and incorporate technology to create effective vertical learning environments. - Can vertical classroom spaces work for every subject?
Yes, vertical classroom spaces can be adapted to suit a wide variety of subjects. For hands-on subjects like science and technology, vertical spaces provide room for interactive experiments, group projects, and easily accessible materials stored at different heights.
Conclusion
The impact of vertical classroom spaces on learning is undeniable. From fostering student engagement and collaboration to enhancing cognitive and psychological well-being, vertical spaces offer a multitude of benefits. As educational needs evolve, adopting vertical classroom designs can help create more dynamic, flexible, and effective learning environments. Embracing this innovative design approach will undoubtedly play a significant role in shaping the future of education.